Copper:
- Coaxial (Thinnet & Thicknet)
- Twisted Pair (UTP & STP)
Fiber:
- Single mode Fiber Optics
- Multimode Fiber Optics
Wireless:
- Short distance: (Bluetooth, Infrared etc.)
- Long distance: (Microwave)
- Very long distance: (Satellite)
COPPER:
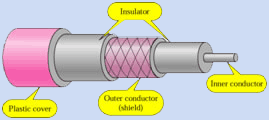 THINNET (10Base2):
THINNET (10Base2):
* RG 58
* Distance limit = 185 m (200m)
* Bandwidth = 10 Mbps
* Less susceptible to EMI than TP.
* Can carry both analog, digital
* Outer cover called sheath, mesh called shield.
* Node per segment: 30
* 0.25 inch
* Connectors:
- BNC: to connect two thinnet
- BNC T-connector: to connect device to the cable.
THICKNET (10Base5)
* RG 8, 11
* 500 m
* Used specially as backbone
* Node per segment: 100
* 0.4 inch
* Connectors:
- AUI (Attachment Unit Interface) also called DIX or DB-15 [15-pin connector]
- N-connector to connect two thicknet (Screw and barrel arrangement).
Note:
Workstation doesn’t connect directly to THICKNET, Transceiver is attached to a THICKNET, the transceiver has port for AUI and an AUI cable (also called drop cable) connect to the workstation)
TWISTED PAIR:
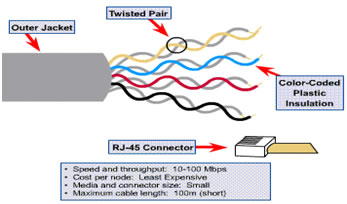
UTP:
- Contain 4 twisted pairs of wires (= 8 wires).
- Inexpensive and widely (easily) available.
- Flexible and light weight
- Easy to work and install
- Susceptible to EMI (Electro Magnetic Field)
- Connector – RJ45 (Registered Jack 45)
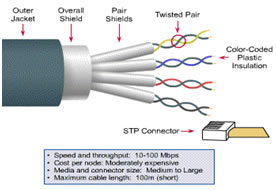
STP:
- Provide extra shield (for pair and overall)
- Expensive than UTP
- Harder to work with.
- Not susceptible to EMI
- STP connector
TWISTED PAIR - CAT 3, 4, 5, 5e, 6, 6a etc.
Cat 1: Currently unrecognized by TIA/EIA. Previously used for POTS telephone communications, ISDN and doorbell wiring. |
Cat 2: Currently unrecognized by TIA/EIA. Previously was frequently used on 4 Mbit/s token ring networks. |
Cat 3: Currently defined in TIA/EIA-568-B, used for data networks using frequencies up to 16 MHz. Historically popular for 10 Mbit/s Ethernet networks. |
Cat 4: Currently unrecognized by TIA/EIA. Defined up to 20 MHz, and was frequently used on 16 Mbit/s token ring networks. |
Cat 5: Currently unrecognized by TIA/EIA. Defined up to 100 MHz, and was frequently used on 100 Mbit/s Ethernet networks. May be unsuitable for 1000BASE-T gigabit Ethernet. |
Cat 5e: Currently defined in TIA/EIA-568-B. Defined up to 100 MHz, and is frequently used for both 100 Mbit/s and 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet networks. |
Cat 6: Currently defined in TIA/EIA-568-B. Defined up to 250 MHz, more than double category 5 and 5e. |
Cat 6a:Currently defined in ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-B.2-10. Defined up to 500 MHz, double that of category 6. Suitable for 10GBase-T |
Cat 7: An informal name applied to ISO/IEC 11801 Class F cabling. Defined up to 600 MHz. This standard specifies four individually-shielded pairs (STP) inside an overall shield. |
Cat 7a: An informal name applied to Amendment 1 of ISO/IEC 11801 Class F cabling. Defined up to 1000 MHz. |
Cable Type |
Max Speed |
Max Distance |
Cost Factor |
Category 5 |
100Mbs |
100m |
1x |
Category 5e |
1000Mbs |
100m |
1x |
Category 6 |
1000Mbs |
100m |
1.3x |
Category 6 |
10,000Mbs |
57m |
1.3x |
Category 6a |
10,000Mbs |
100m |
2x |
OPTICAL FIBER:
- Core is of glass or fiber (surrounded by cladding)
(cladding trap the light in the core) - All covered by plastic coating (buffer) to save it from physical damage or moisture.
- Light travel through the optical media by the way of total internal reflection.
- Can have 1 to 1000 fibers
- Bandwidth: upto 10 Gbps
- Distance: thousand of Kilo meters
- Not affected by noise (EMI)
- Adding additional node is difficult
- Require highly skill professional to install
- Connector: SC and ST
Types of Fiber Optics:
a) Single mode (Mono mode):
- Range: upto thousand of kilometers without repeater.
- Bandwidth: upto 10 Gbps
- Source: Laser light
b) Multi mode (Mono mode):
- Multiple channel (fibers)
- 3 km (without repeater)
- 10 Gbps
- Source: LED and laser light
Wireless:
- Can work where cable is not possible
- Provide mobility
- Susceptible to rain or atmospheric variations
Indore: Bluetooth, Infrared
LAN: WLAN (Wireless Access Point)
Medium Range: GSM, CDMA, WIMAX: 200 m – 5 Km.
Long Range: Microwave (5 Km – 100 Km)
Very Long Range: Satellite (Across Continents)
How to Create straight and cross cable (video below):

